Self-floating Rubber Tube
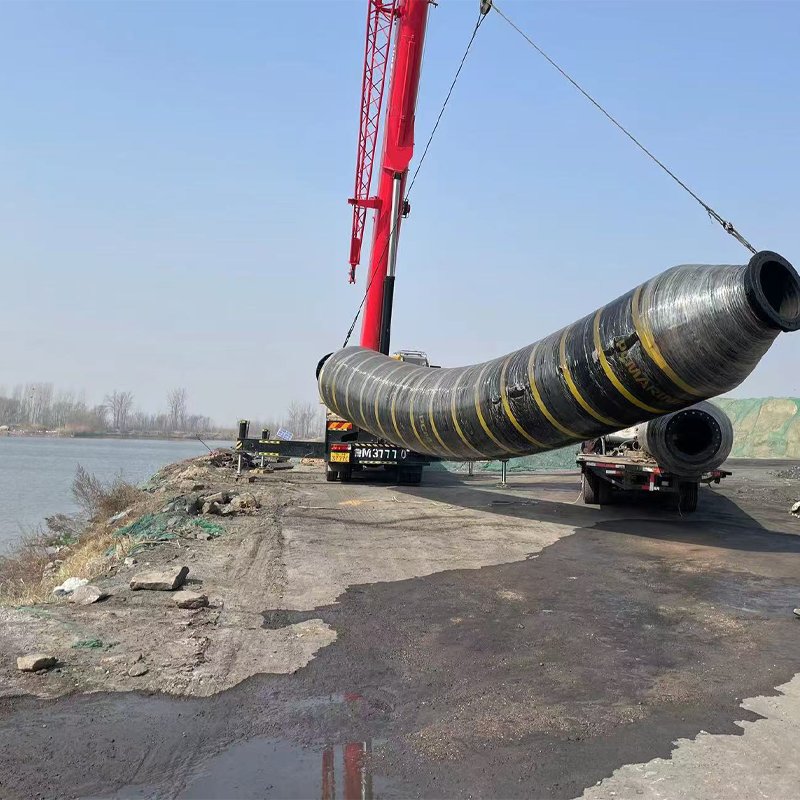

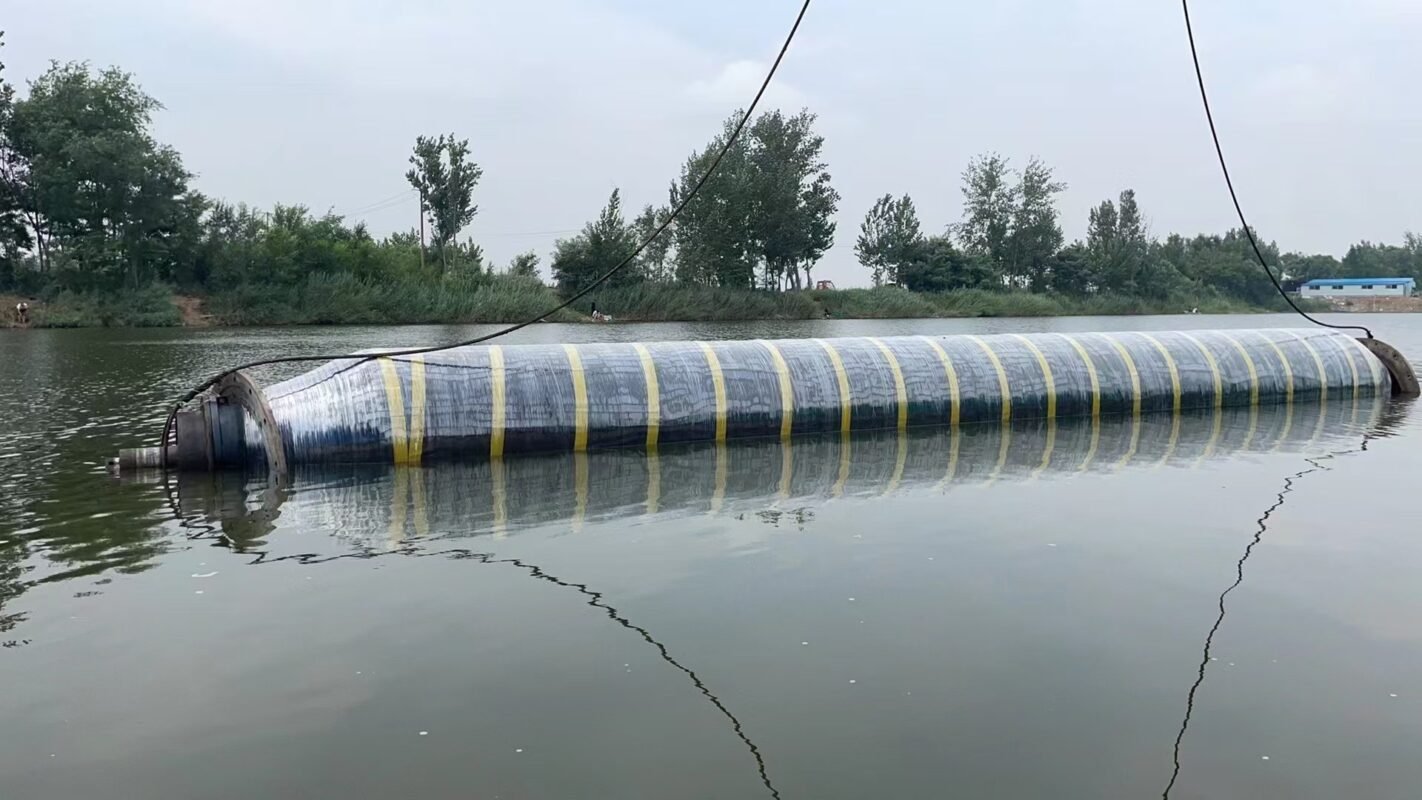
Self-floating rubber tube is a flexible pipe with a special design. Its unique feature is that it can float independently in water without the need for additional buoyancy devices.
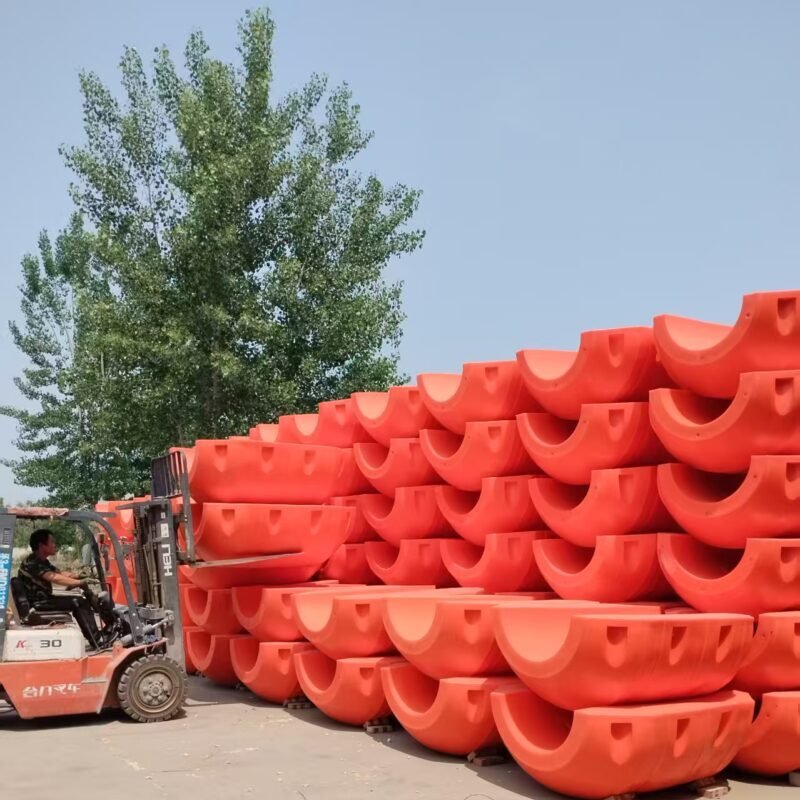
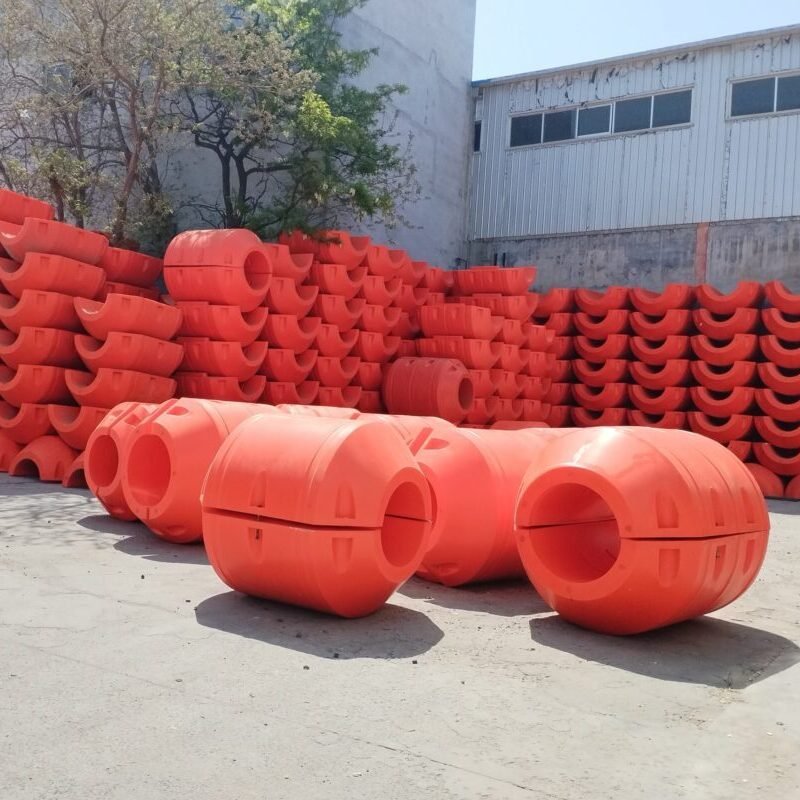
Structure:Inner Layer: Made of corrosion-resistant synthetic rubber material, it can well adapt to various conveying media, including common water, oil, weak acid, and weak alkali liquids.Reinforcement Layer: Constructed from high-tension polyester fibers, this structure provides reliable compressive and tensile strength for the rubber tube.Buoyant Layer: Closed-cell foaming materials, such as PE foam, are used to ensure that the rubber tube can obtain stable buoyancy in water.Outer Layer: Anti-aging rubber is used, and ultraviolet stabilizer is added to effectively extend the service life of the rubber tube in outdoor environments.

Features:Adaptive Floating: Whether in static or dynamic operating conditions, the self-floating rubber tube can always maintain a specific position on the water surface, avoiding friction with the water bottom.Rapid Deployment: Since there is no need to install additional floating bodies, it can be quickly put into use in emergency drainage and other situations.Strong Weather Resistance: Its operating temperature range is -30℃ to 80℃, enabling it to adapt to most climatic conditions.
Selection Parameters:Caliber:Determine the appropriate caliber size according to actual flow requirements.Working Pressure:Select a working pressure that matches the actual working conditions.Buoyancy Margin:Generally, during the design process, an additional 20% buoyancy at full load is ensured to prevent the pipe from submerging due to factors like waves.Wear Resistance Index:Determine the required wear resistance index based on the characteristics of the specific conveying medium.
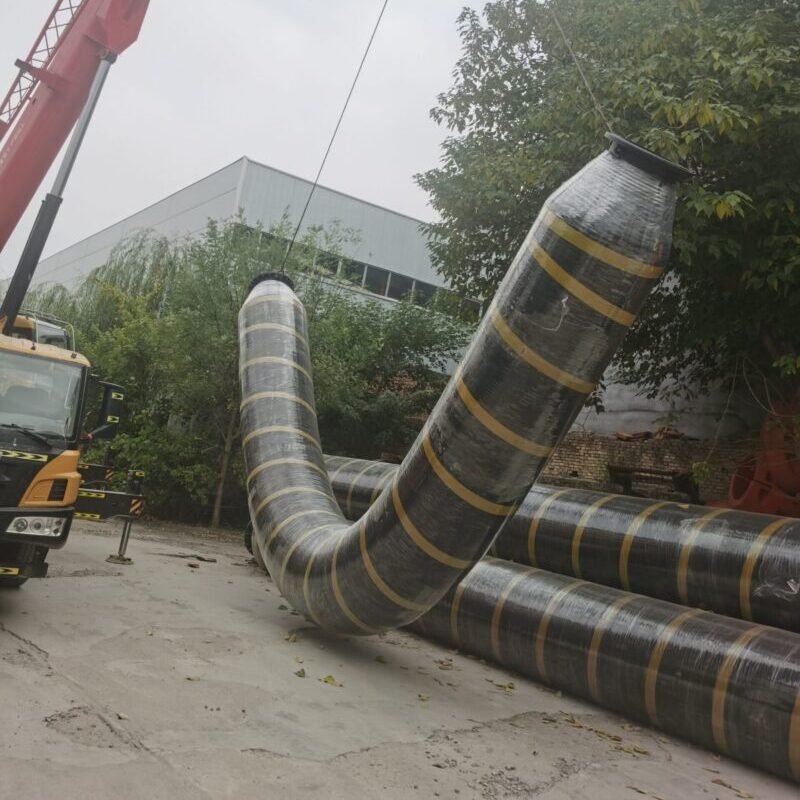
Use and Maintenance:Installation Precautions:Before installation, carefully check the water environment to ensure there are no sharp obstacles, avoiding scratching the rubber pipe.When bending the rubber pipe, its bending radius should be greater than 5 times the pipe diameter to prevent kinking.The anchoring end should be flexibly connected to reduce stress concentration issues.Maintenance Recommendations:Regularly flush the deposits on the inner wall of the rubber tube to maintain good flow rate.After using for a period of time, appropriately rotate the pipe body to prevent the wear-resistant layer from being worn through due to the long-term erosion of the same surface by the medium.Regularly check whether there are cracks, bulges, and other problems on the outer layer of the rubber pipe. If any issues are found, repair them in a timely manner.When the rubber tube is out of use for a long time, clean it and keep it dry, while avoiding deformation caused by stacking.