Maintenance and Care of HDPE Pipes
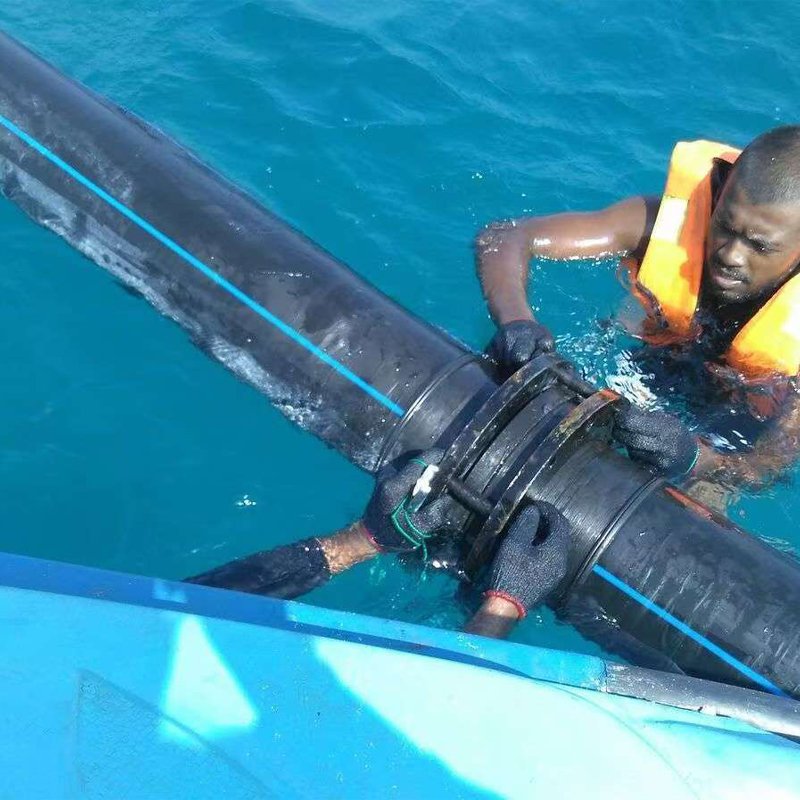

HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) pipes are widely used in fields such as water supply and drainage, gas transmission, and industrial conveying due to their excellent corrosion resistance, flexibility, light weight, and long service life. However, to ensure their long-term stable operation, proper maintenance and upkeep are crucial. Below is a comprehensive guide to HDPE pipe maintenance and upkeep, which can be divided into four parts: daily maintenance, regular inspections, fault repair, and long-term shutdown maintenance.
I. Daily Maintenance and Operation Standards
The core of daily maintenance lies in standardized operations to prevent problems from occurring.
1. Standardized Start-up and Shutdown Operations:
• Avoid Sudden Pressure Changes: When opening or closing valves, operate slowly to prevent water hammer (or air hammer) effects. Sudden pressure changes can impact the pipeline system, damaging pipes and connections.
• System Venting Before Startup: Before conveying liquids,务必 open the vent valve at the highest point of the system to expel all air, avoiding air hammer and unstable flow.
2. Control Operating Parameters:
• Temperature: Ensure that the medium and ambient temperatures are within the allowable working temperature range of HDPE pipes (usually -40°C to +60°C, refer to product specifications for specifics). Avoid prolonged exposure to high temperatures to prevent reduced pressure resistance and lifespan.
• Pressure: The operating pressure must not exceed the rated design pressure of the pipeline system.
• Medium: Confirm that the conveyed medium is compatible with HDPE material. Although HDPE is resistant to most chemical corrosion, caution is still needed with certain strong oxidants, hydrocarbon solvents, etc.
3. External Environmental Protection:
Avoid direct sunlight: HDPE is sensitive to ultraviolet (UV) rays, and prolonged exposure can cause aging and brittleness. For exposed or overhead-installed pipes, shading measures should be taken (such as applying UV-resistant coatings, wrapping with protective layers, or using black pipes, as carbon black is an effective UV stabilizer).
• Prevent mechanical damage: Warning signs should be installed for ground-level exposed pipes to avoid collisions or scratches from vehicles or heavy objects. In areas prone to external impact, protective sleeves or guards should be added.
II. Regular Inspections
Establish a regular inspection system to promptly identify potential issues.
1. Visual Inspection:
• Exposed pipes: Check the pipe surface for obvious scratches, cracks, dents, bulges, or discoloration (especially whitening and brittleness caused by sun exposure).
• Buried pipes: Regularly inspect exposed sections, parts within valve pits, and inspection wells for abnormal deformation or damage.
• Supports and hangers: Check if the support system is secure, with no looseness, detachment, or damage. Ensure pipe clamps are not too tight to avoid restricting thermal expansion and contraction of the pipes.
2. Joint Inspection:
• Hot-melt joints: Check if the weld is smooth and symmetrical, with no signs of false welding or over-welding (such as uneven flash or porosity).
• Electrofusion joints: Check if the observation holes have popped out normally and if the joints are aligned.
• Flange connections: Check if bolts are tightened, and if gaskets are aged or leaking.
3. Performance Inspection:
• Pressure testing: Pressure tests (strength test and tightness test) should be conducted after system installation or major repairs. In daily maintenance, segmental pressure testing can also be performed if a section of the pipe is suspected to have issues.
• Flow and pressure monitoring: Record the daily operating pressure and flow of the system. Abnormal drops or fluctuations may indicate blockages, leaks, or scaling inside the pipes.
III. Common Faults and Repair Methods
When problems are detected, appropriate corrective measures should be taken promptly.
1. Minor Scratches:
◦ Situation: There are slight scratches on the pipe wall surface that do not damage the structural layer.
◦ Repair: Use a dedicated plastic welding gun with HDPE welding rods of the same material to fill and repair, then smooth the surface by grinding.
2. Small Holes or Cracks:
◦ Situation: Local small leakage points appear.
◦ Repair: ■ Clamp Repair: Use a dedicated HDPE pipe repair clamp (stainless steel sleeve + rubber seal), which is the most commonly used and quick method. ■ Welding Repair: For positions suitable for welding, the damaged part can be cut off and repaired using hot-melt butt welding or electrofusion sleeves.
3. Severe Damage or Breakage:
◦ Situation: The pipe has large-scale rupture or severe deformation.
◦ Repair: ■ Cut and Replace: This is the most thorough method. Completely cut out the damaged section and replace it with a new pipe section and two electrofusion sleeves or one butt weld joint. ■ Lining Repair: For situations where excavation is inconvenient, non-excavation lining repair technology can be adopted, inserting a new HDPE pipe into the old pipe to form a \”pipe within a pipe\”.
4. Joint Leakage:
◦ Hot-Melt/Electrofusion Joint Leakage: Usually cannot be repaired and must be cut off and re-made.
◦ Flange Joint Leakage: First try to tighten the bolts. If ineffective, shut down the system, depressurize, and replace the flange gasket.
IV. Maintenance for Long-Term Shutdown
If the pipeline system needs to be shut down for a long period, the following measures should be taken:
1. Drain the Medium: Completely drain the liquid (especially water) in the pipeline to prevent freezing cracks in winter or bacterial growth and odor caused by long-term stagnation of static water.
2. Clean the Pipeline: For pipelines that have transported easily deposited or corrosive media, flushing and cleaning should be performed before shutdown.
3. Block and Protect: Block the pipe ends to prevent debris and small animals from entering.
4. Depressurize: Ensure the system is completely depressurized so that the pipeline is stored under no stress.
5. Regular Inspection: Even when shut down, it should be included in the regular inspection scope, especially visual inspections of exposed parts.
Core Summary
• Prevention First: Standard operations and regular inspections are the lowest-cost and most effective maintenance methods.
• Handle with Care: HDPE pipes have good flexibility but are afraid of scraping, sun exposure, drastic temperature changes, and pressure shocks.
• Professional Repair: Repair of HDPE pipes (especially welding) must be carried out by trained professionals using dedicated tools to ensure repair quality.
• Record and Archive: Establish a complete pipeline file, including installation drawings, welding records, inspection reports, and maintenance history, which is very valuable for long-term maintenance management.
Following the above maintenance and care regulations can maximize the advantages of HDPE pipes and ensure their safe, reliable, and long-term operation.