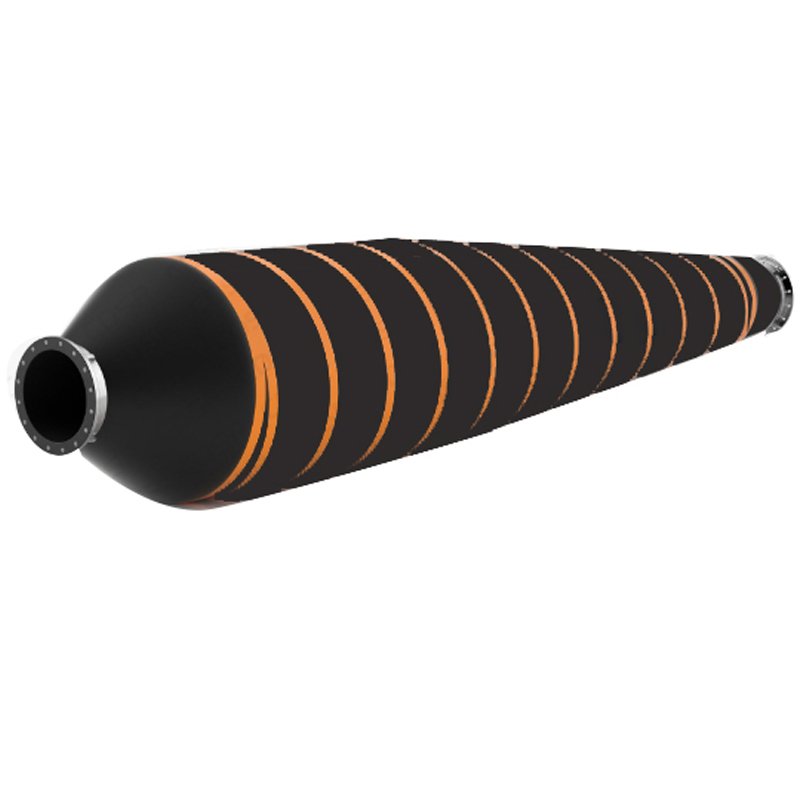
How to testing the flexibility of tapered floating hose
Testing the flexibility of tapered floating hose requires a comprehensive evaluation based on industry standards (such as OCIMF, ISO) and practical application needs. Here are detailed testing steps and precautions:
1. Preparation before Testing
Confirm standards: Refer to relevant industry standards (e.g., OCIMF ‘Floating Hose Guidelines’, ISO 10823) or customer requirements.
Sample selection: Choose representative samples (new hoses and those that have undergone aging tests).
Environmental conditions: Conduct tests under standard temperature and humidity conditions (typically 20±5°C) to avoid extreme temperatures affecting results.
2. Static Flexibility Test
Bend radius test:
Slowly bend the hose to the manufacturer’s specified minimum bend radius (e.g., 6 times the pipe diameter). Observe for creases, cracks, or delamination.
Maintain the bent state for 1 hour, then release and check for permanent deformation (residual deformation should be <5%).
Hanging test:
Vertically hang the hose and measure the natural sag, comparing it to standard values.
3. Dynamic Flexibility Test
Repeated bending test:
Use mechanical devices to simulate the hose’s movement in waves (e.g., ±30° reciprocating bending 1000 times). Check for joint loosening, outer rubber wear, or inner layer cracking.
Twisting test:
Fix one end and apply torque to the other end (e.g., ±180° twisting). Evaluate the anti-kinking ability.
4. Low-Temperature Flexibility Test
Low-temperature bending:
Place the hose in a freezer at -20°C (as per specifications) for 24 hours, then immediately bend it. Check for brittleness or hardening.
Impact test (optional):
Drop a weight onto the hose at low temperatures to assess brittleness resistance.
5. Flexibility Under Pressure Cycles
Pressurized bending:
Bend the hose while pressurized (e.g., at 50% working pressure). Observe if the flexibility decreases due to pressure addition.
6. Material Performance Test
Shore hardness: Measure the hardness of the outer rubber layer using a hardness tester (change value should be <10%).
Tensile test: Detect the elongation at break of the rubber material (usually required ≥300%).
7. Real-world Condition Simulation
Buoyancy test in water:
Float the hose on the water surface and simulate wave and tidal movements. Observe the bending adaptability.
Tow test (if applicable):
Evaluate the dynamic response of the hose during low-speed towing.
8. Data Recording and Evaluation
Record parameters for each test (bending angle, cycle count, temperature, etc.) and failure modes.
Compare initial and post-test performance (e.g., change in bending force, leakage rate).
9. Safety Precautions
Avoid exceeding the hose’s nominal minimum bend radius.
Maintain a safe distance during high-pressure tests to prevent burst risks.
Wear protective gear during low-temperature operations.
10. Certification and Reporting
For third-party certification needs (e.g., DNV, ABS), tests must be conducted by an accredited laboratory and a report issued.
By following these methods, the flexibility of tapered floating hose can be comprehensively assessed to meet requirements for wave resistance, fatigue resistance, and low-temperature operation. Actual testing should adjust parameters according to hose specifications, prioritizing manufacturer-provided test guidelines.