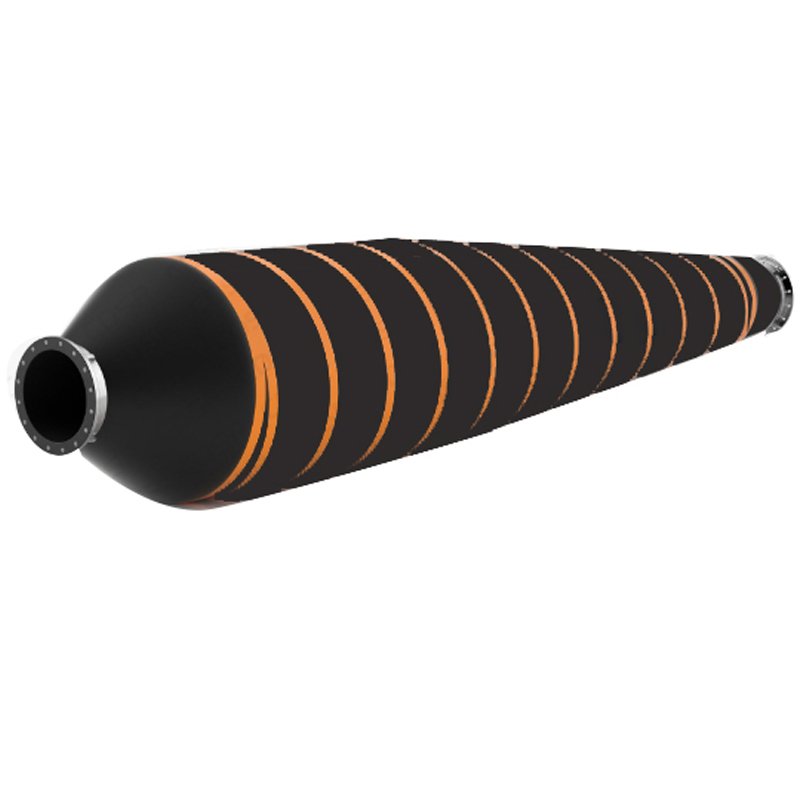
How to testing the abrasion resistance of tapered floating hoses
Testing the abrasion resistance of tapered floating hoses requires combining standard test methods with actual usage conditions to ensure their durability in real applications. Here are detailed testing methods and steps:
1. Define Testing Standards
– Refer to international standards such as ISO 4649 (rubber abrasion resistance test), ASTM D5963 (marine hose abrasion resistance), or API 17K (dynamic flexible pipe specifications).
– Industry requirements: Specific standards may exist for the oil, marine, or dredging industries, which should be prioritized.
2. Testing Methods
(1) Laboratory Tests
– Abrasion Tester (e.g., Taber Abraser)
– Fix the hose sample on the machine and apply pressure using rotating sandpaper or abrasive wheels.
– Measure weight loss or thickness reduction after a certain period.
– Key parameters: load (e.g., 10N), rotation speed (e.g., 60 rpm), cycle count (e.g., 1000 cycles).
– Reciprocating Friction Test
– Simulate friction between the hose and ships, docks, or other surfaces.
– Use a linear friction machine to repeatedly scrape the hose surface and observe wear.
(2) Simulated Condition Tests
– Dynamic Water Abrasion Test
– Place the hose in water containing sand or abrasive particles (simulating dredging or marine environments).
– Test the effects of flow rate and particle concentration on the outer layer (usually rubber or polyurethane).
– Bend Friction Test
– Simulate the floating state of the hose in waves, testing friction at bending points with buoys or other components.
(3) Field Tests
– Install the hose in actual usage environments and regularly check wear (e.g., every 3 months).
– Record environmental factors: salinity, water flow speed, rough surfaces it contacts.
3. Key Evaluation Metrics
– Wear Depth: Measure thickness changes before and after testing using a micrometer.
– Weight Loss: Weigh using an electronic balance accurate to 0.1 mg.
– Surface Condition: Inspect visually or under a microscope for cracks, peeling, delamination.
– Retained Mechanical Properties: Test tensile strength and elongation post-wear to ensure compliance.
4. Accelerated Aging Test
– Combine UV exposure, salt spray (ASTM B117), and temperature cycling to evaluate performance degradation of the abrasion-resistant layer over time.
5. Comparative Analysis
– Compare with similar products or historical data to assess abrasion resistance levels.
– For example: Under identical conditions, Brand A hose wears 0.5 mm, while Brand B wears 1.0 mm.
6. Test Report Content
– Testing methods, equipment, and standards used.
– Environmental conditions (temperature, humidity, etc.).
– Wear data (charts + values).
– Conclusions and improvement suggestions (e.g., adding protective layers or changing materials).
Notes
– Sample Consistency: Average multiple samples from the same batch.
– Realistic Simulation: Laboratory tests may not fully replicate complex marine environments; field data should be considered.
– Safety Margin: Recommend abrasion resistance test results exceed actual needs by 20%-30%.
By following these methods, the abrasion resistance of tapered floating hoses can be comprehensively evaluated, ensuring their lifespan in dynamic marine environments.