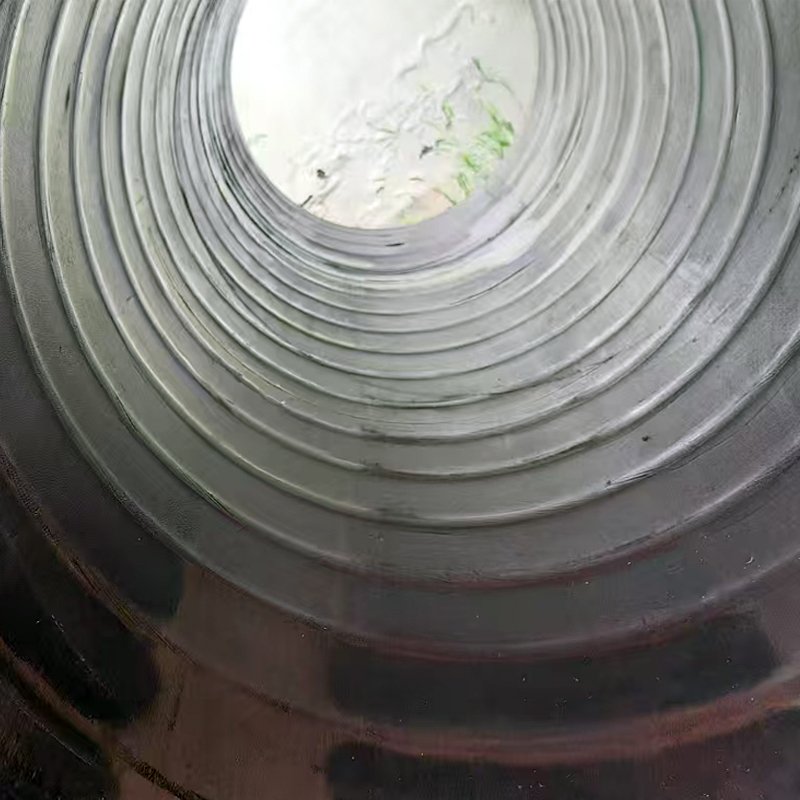
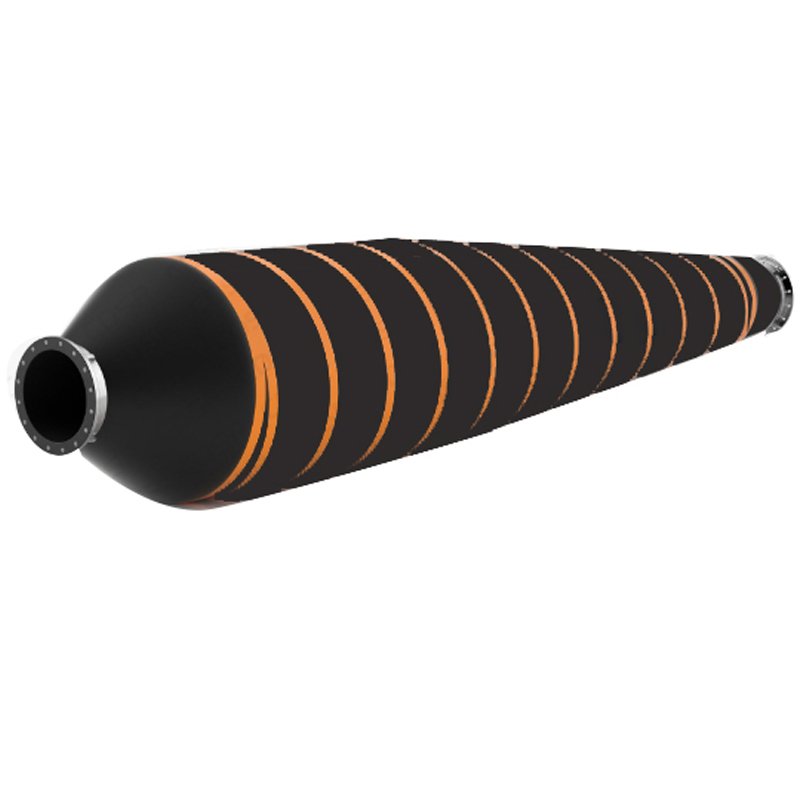
How to choose the right tapered floating hose

Choosing the right tapered floating hose involves considering several factors, including the application, material, size, buoyancy requirements, and environmental conditions. Here is a detailed selection guide:
1. Clarify Application Needs
– Purpose: Used for marine/ocean oil transfer, chemical transportation, dredging projects, water firefighting, etc.?
– Medium: Transporting oil, chemicals, slurry, or freshwater? Different media have different material requirements.
– Working Environment: Seawater (corrosion-resistant), freshwater, extreme temperatures, UV exposure, wave impact, etc.?
2. Key Parameter Selection
(1) Size and Structure
– Diameter (internal): Choose based on flow requirements (e.g., 6″, 8″, 10″), matching pump and pipeline specifications.
– Tapered Design:
– Typically one end is larger, the other smaller, facilitating connection to different-sized pipes or equipment.
– Confirm the length and diameter change ratio of the tapered section (e.g., 10″→8″).
– Length: Choose based on actual laying distance, common single-section lengths are 10-20 meters, multiple sections can be connected.
(2) Material
– Inner Layer:
– Oil/Chemical Resistant: NBR (nitrile rubber), EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer).
– Wear-Resistant: Polyurethane (PU) or high-density rubber (for dredging).
– Reinforcement Layer: Multiple layers of high-strength polyester fibers or steel wire braiding, ensuring pressure resistance and tensile strength.
– Outer Layer: Anti-UV, weather-resistant synthetic rubber or PVC, anti-salt mist corrosion in seawater environments.
– Buoyancy Material: Closed-cell foam (e.g., PE foam) or inflatable design, calculate if the buoyancy is sufficient to support the weight of the pipe and medium.
(3) Working Pressure
– Choose based on pumping pressure (e.g., 0.3MPa, 0.6MPa), leaving a margin to avoid bursting.
(4) Buoyancy Requirements
– Calculate required buoyancy: Ensure the hose floats on the surface and supports the weight of the medium.
– Float Spacing: Some designs feature external floats, confirm if float spacing is reasonable.
3. Special Functional Requirements
– Wear Resistance: Dredging hoses need reinforced wear-resistant layers (e.g., ceramic lining).
– Fire/Static Protection: Oil transfer hoses must comply with standards like API 1529.
– Flexibility: High flexibility design for frequent bending applications.
– Visibility: Bright colors (orange/yellow) or reflective strips for easy identification on water.
4. Certification and Standards
– Industry Standards:
– Petroleum Industry: API 1529, OCIMF.
– Firefighting: EN 14540.
– Environmental: Non-polluting materials (e.g., REACH).
– Third-Party Certification: DNV, ABS, CE, etc.
5. Brand and Supplier Evaluation
– Reliability: Choose reputable brands (e.g., Trelleborg, ContiTech, Dunlop).
– After-Sales Service: Does the supplier offer technical support and quick replacement services?
– Cost: Balance budget and lifespan (cheap products may not be durable).
6. Environmental Adaptability Testing
– Weather Resistance: Has it undergone UV aging, salt mist testing?
– Low-Temperature Performance: Maintains flexibility in cold environments?
– Dynamic Load: Stability under wave or water current impact.
7. Installation and Maintenance
– Connection Method: Flange, quick coupler, or clamp? Ensure sealing.
– Maintenance Convenience: Is it easy to clean and repair?
Recommended Steps
1. List specific needs (medium, pressure, length, etc.).
2. Consult suppliers for technical data sheets (TDS) and certification documents.
3. Request samples to test key performance (buoyancy, chemical resistance).
4. Compare 3-5 options, make a decision based on cost-effectiveness.