Comparative Analysis of Ultra-High Molecular Weight Pipe and PE Pipe
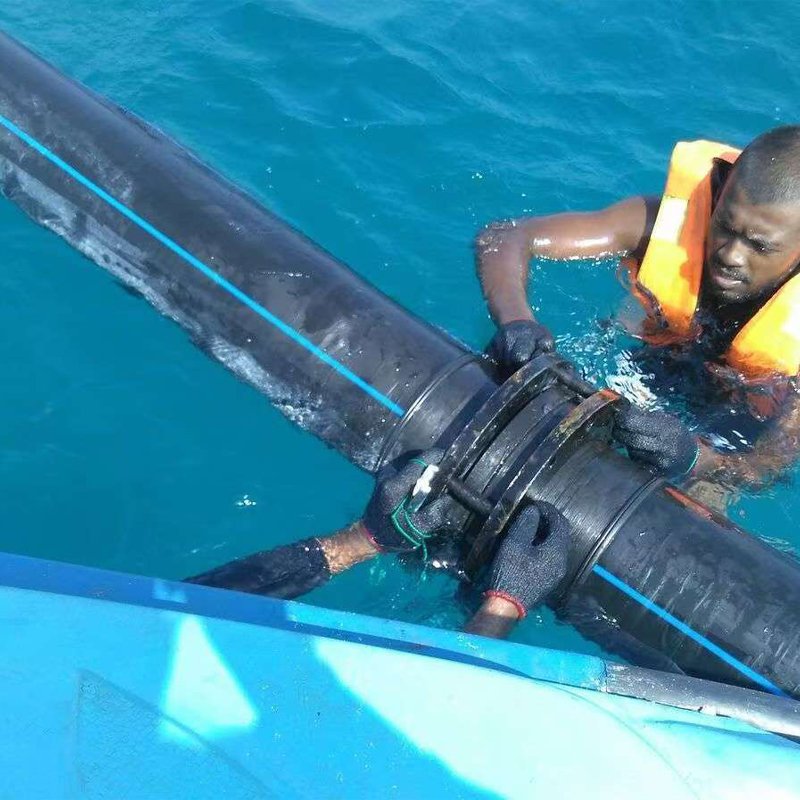

Ultra-high molecular weight pipes (often referred to as UHMWPE pipes, i.e., ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene pipes) and PE pipes (polyethylene pipes) both contain the term ‘polyethylene’ in their names, but they are two types of pipe materials with significant differences in performance, application scenarios, and costs. The most fundamental difference lies in the molecular weight of polyethylene, as well as the material grade determined by this molecular weight.
To help quickly grasp the core information, the following table compares their key differences:
Comparison Dimensions
Ultra-High Molecular Weight Pipe (UHMWPE Pipe)
Ordinary PE Pipe
Essential Definition
Thermoplastic engineering plastic pipe with a molecular weight >1.5 million
General plastic pipe with a lower molecular weight of polyethylene
Core Performance
Excellent wear resistance (4-7 times that of steel pipes and 10 times that of ordinary PE pipes); strong impact resistance (with better performance in low-temperature environments); low friction coefficient, Has self-lubricating properties and is less prone to scaling (possesses self-lubricating properties and is less prone to scaling)
Good toughness and corrosion resistance, but wear resistance and impact resistance are far inferior to ultra-high molecular weight pipes
Typical Applications
Harsh wear/corrosion environments in industrial fields: – Mining: Tailings and ore pulp transportation; – Power: Fly ash transportation; – Dredging: Slurry transportation; – Chemical industry: Transportation of corrosive media
Civil and general industrial transportation scenarios: – Urban water supply and drainage; – Gas transportation; – Agricultural irrigation; – Communication cable sheathing
Cost and Economy
Higher unit price, but can significantly reduce long-term comprehensive costs due to ultra-long service life
Lower unit price, with Highlight cost-effectiveness (outstanding cost-effectiveness), making it the standard selection for civil and general municipal fields
📝 How to Select Based on Requirements
After clarifying the core differences, you can make precise decisions by combining specific project needs:
1. Scenarios where Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) Pipes Should Be Prioritized
When the medium being transported is highly abrasive or corrosive, or when operating conditions are extremely harsh (such as low-temperature environments, high impact loads), UHMWPE pipes should be the first choice. Specific examples include:
– Transporting media containing solid particles or slurries, such as mineral powder, ash residue, and mud;
– Transporting strongly corrosive chemical media like concentrated acids, strong alkalis, and salt solutions;
– Industrial projects with extremely high requirements for pipe service life, aiming to significantly reduce maintenance frequency and replacement costs.
2. Scenarios where Ordinary PE Pipes Should Be Prioritized
For the vast majority of routine transportation tasks, especially in civilian and municipal engineering, ordinary PE pipes are a more economical and technically mature choice. Specific examples include:
– Laying urban water supply networks and drainage/sewage systems;
– Low-pressure gas transportation such as natural gas and town gas;
– Agricultural irrigation pipes and cable protection sleeves.
💡 Purchase and Usage Notes
During actual purchase and use, the following points need special attention:
1. Confirm Material Authenticity: There are cases in the market where ordinary PE pipes or recycled materials are Impersonate (mǒochōng – impersonate/fake) UHMWPE pipes. When purchasing, it is essential to require suppliers to provide raw material molecular weight test reports (the standard requires molecular weight ≥1.5 million) and prioritize reputable well-known brands.
2. Pay Attention to Connection Method Compatibility: Due to material property limitations, UHMWPE pipes mostly use flange connections or dedicated electro-fusion welding, which have higher requirements for construction processes; whereas hot-melt butt welding technology for ordinary PE pipes (especially HDPE pipes) has been standardized, making construction more universal and convenient.
3. Match Operating Temperature Range: UHMWPE pipes have excellent low-temperature resistance and can be used in extreme low-temperature environments as low as -269°C, with anti-impact performance not deteriorating but actually improving at low temperatures, which is one of its core advantages; ordinary PE pipes also have certain low-temperature resistance (e.g., conventional models can withstand -40°C), but their performance will significantly deteriorate as temperature decreases.
4. Comprehensive Evaluation of Full-Life Cycle Cost: When selecting, do not only compare initial purchase prices. In severely abrasive conditions, steel pipes usually need maintenance or replacement every 1-2 years, while the designed service life of UHMWPE pipes can reach over 50 years, and their long-term comprehensive cost (including maintenance costs, downtime losses, etc.) is often lower.
In summary, if the project faces harsh challenges such as wear, corrosion, or low-temperature impact, UHMWPE pipes are a more reliable technical solution; if the application scenario is for routine water and gas transportation with ordinary requirements, ordinary PE pipes with high cost-effectiveness and mature technology are a more suitable choice.
If you can provide specific transportation media, operating environment (such as temperature, pressure, whether containing particles, etc.), I can further provide you with precise selection recommendations.