Applications of HDPE Pipes
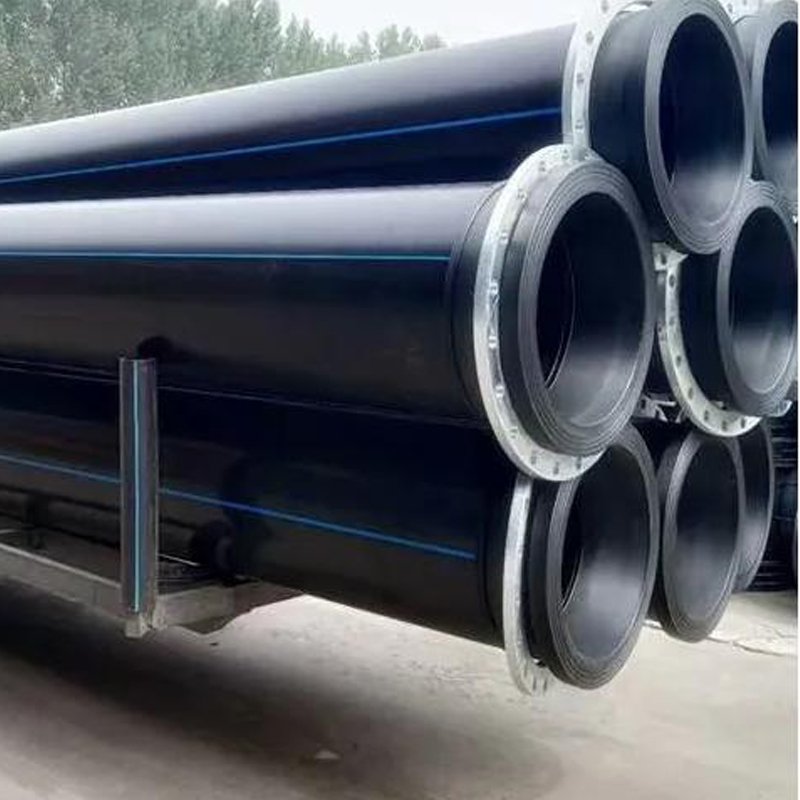

HDPE pipes (High-Density Polyethylene Pipes) are widely used in modern engineering due to their unique properties, covering almost all fields from municipal to industrial, and from above-ground to underground. The following are the main application scenarios of HDPE pipes, which are explained in detail in several categories:
I. Municipal Engineering Field (The Core Application)
This is the largest and most traditional application market for HDPE pipes.
1. Water Supply System:
◦ Municipal Main Water Supply Pipes: Used as branch lines of the city’s main water supply network, replacing traditional cast iron pipes and concrete pipes.
◦ Indoor and Outdoor Drinking Water Pipes: Due to being non-toxic, odorless, and not prone to scale formation, they fully meet the standards for drinking water transportation and are commonly used for cold and hot water pipes in building interiors.
◦ Direct Drinking Water Pipes: For occasions with extremely high hygiene requirements.
2. Drainage and Sewage System:
◦ Municipal Sewage Pipes: Strong corrosion resistance, effectively resisting chemical substances in domestic sewage and industrial wastewater.
◦ Rainwater Discharge Pipes: Lightweight and convenient for construction, used in urban rainwater collection and discharge systems.
◦ Residential and Commercial Area Drainage: Sewage and rainwater networks in residential communities and commercial areas.
3. Gas Transmission:
◦ Medium and Low Pressure Gas Networks: HDPE pipes have excellent creep resistance and toughness, making them an ideal choice for transmitting natural gas and coal gas, with high safety and long service life.
II. Industrial Field
1. Chemical Industry:
◦ Used to transport various corrosive media such as acids, alkalis, and salts, because HDPE has excellent chemical corrosion resistance.
2. Mining and Metallurgical Industries:
◦ Slurry Transportation: Good wear resistance, used for transporting abrasive media such as tailings, mud, and coal powder.
◦ Industrial Ventilation: Used to exhaust corrosive gases.
3. Seawater Transmission and Aquaculture:
◦ Corrosion-resistant to seawater, seawater desalination plants’ raw water intake, power plant cooling water circulation, and water supply and drainage systems for coastal aquaculture.
4. Food and Pharmaceutical Industries:
◦ Transport some fluids with high hygiene requirements, such as beverages and milk, because their inner walls are smooth and less likely to breed bacteria.
III. Agricultural Field
1. Farmland Irrigation:
◦ This is a very important application of HDPE pipes. They are widely used in the main pipes and branch pipes of drip irrigation and sprinkler irrigation systems, effectively saving water resources.
◦ Advantages: Good weather resistance (UV resistance), good flexibility, low cost, and resistance to chemical corrosion in soil.
2. Forestry Irrigation:
◦ Similarly suitable for irrigation systems in complex terrains such as mountainous areas and forest lands.
IV. Special and Emerging Applications
1. Power and Communication Cable Protection:
• Cable Conduit Pipes: HDPE silicon core pipes, plum blossom pipes, corrugated pipes, etc., are widely used for underground laying protection of optical fiber, communication cables, and power cables, providing insulation, moisture resistance, and mechanical damage prevention.
2. Underground Utility Tunnels (Integrated Utility Tunnels):
• In urban underground integrated utility tunnels, HDPE pipes are often used as carriers for various pipelines (such as potable water, reclaimed water, and drainage).
3. Non-Destructive Construction (Jacking and Pulling Pipes):
• Due to its excellent toughness and the ability to be welded into ultra-long pipe sections, HDPE pipe is highly suitable for installation using non-destructive techniques (such as directional drilling). This significantly reduces disruption to ground traffic and the environment and lowers costs.
4. Landfill Leachate Collection:
• Used for collecting and treating toxic leachate generated in landfills, where its corrosion resistance is crucial.
5. Ground Source Heat Pump Systems:
• As buried ground heat exchangers, HDPE pipes are buried underground to facilitate heat exchange between circulating fluid and soil. Its good thermal conductivity and long service life make it an ideal choice for this application.
Summary: Why is HDPE pipe so widely applied? The fundamental reason lies in its excellent material properties:
• Corrosion Resistance: No anti-corrosion treatment is required, with a service life of up to 50 years or more.
• Good Toughness and Impact Resistance: It is not prone to breakage even under conditions such as earthquakes and foundation settlement.
• Smooth Inner Wall: Low water resistance, high flow rate, and no scaling.
• Light Weight: Convenient transportation and installation, leading to high construction efficiency.
• Reliable Connection: Uses heat fusion butt welding or electrofusion connection, ensuring joint strength is the same as the pipe body itself with no leakage risk.
• Good Flexibility: Can be coiled, suitable for non-destructive construction, and adaptable to complex terrains.
In short, HDPE pipe is a successful example of \”replacing steel with plastic\”. Due to its safety, durability, economy, and environmental friendliness, it has become an indispensable key material in modern infrastructure construction.