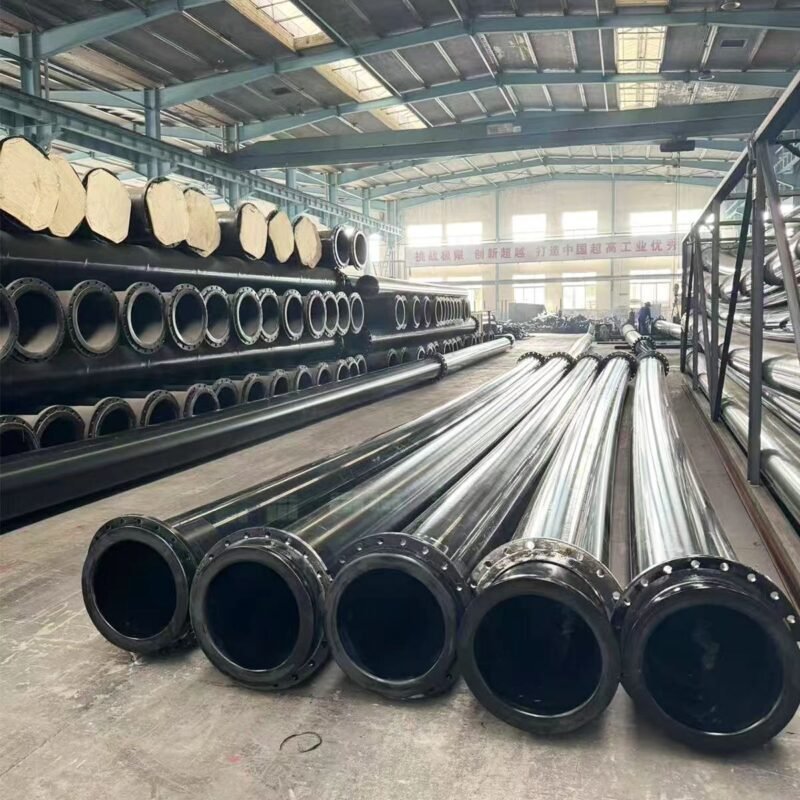
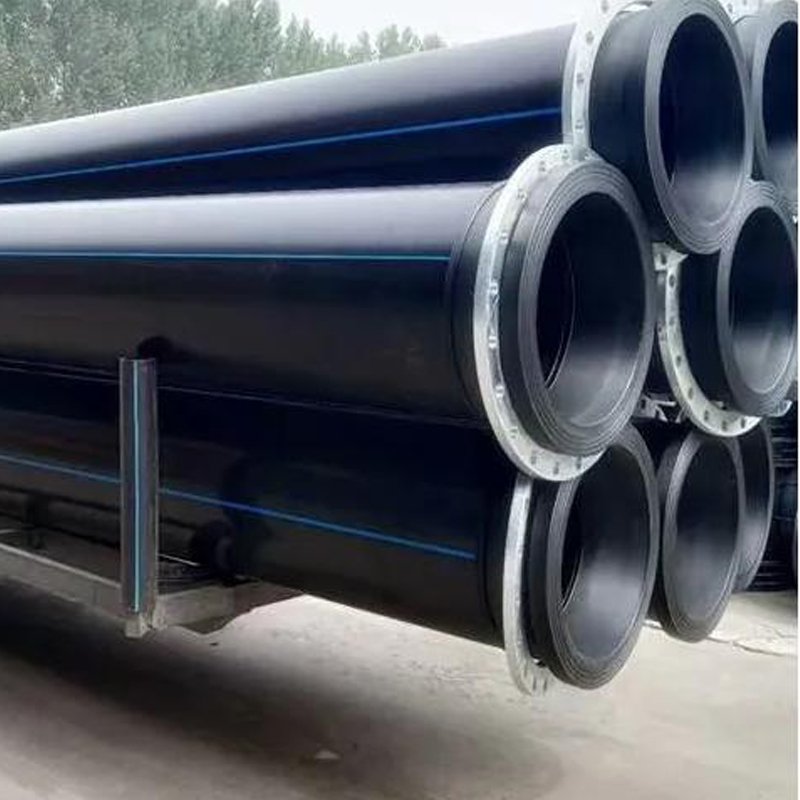
Analysis of Application Fields and Advantages of Ultra-High Molecular Weight Pipe

Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMW-PE) pipes, with their exceptional performance, hold irreplaceable application value in numerous traditional and high-tech fields. Their core characteristics include: extremely high wear resistance (7 times that of carbon steel), excellent self-lubrication, good impact resistance, stable chemical corrosion resistance, low density (lighter than water), and a tendency not to scale.
Below is a detailed Sort out and explanation of their application areas:
一、Core Industrial Fields
1. Mining and Mineral Processing
• Applications: Slurry conveying pipelines (including tailings, concentrates, and coal slurry conveying), flotation machine components, sand pump linings.
• Advantages: Exceptional wear resistance, with a service life far exceeding that of steel pipes (by several to ten times), significantly reducing downtime for replacement and thus lowering comprehensive costs; lightweight, facilitating installation and construction.
2. Coal Industry
• Applications: Water-coal slurry conveying pipelines, underground water supply and drainage pipelines, various slurry conveying pipelines in coal washing plants.
• Advantages: Combines wear resistance and impact resistance, with excellent corrosion resistance, capable of withstanding the harsh physical and chemical environments in coal mining processes.
3. Dredging Engineering
• Applications: Mud discharge pipelines of dredgers, river silt cleaning conveying pipelines.
• Advantages: Excellent wear resistance to media containing large amounts of mud, sand, and gravel; smooth pipe walls result in low fluid resistance, improving conveying efficiency; lightweight, facilitating installation and mobile operations on ships.
4. Power and Thermal Energy
• Applications: Fly ash conveying pipelines, ash removal and slag discharge pipelines, circulating water pipelines.
• Advantages: Wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant, effectively addressing industry pain points such as metal pipes being worn through and easily scaling and clogging.
5. Chemical and Petroleum Industries
• Applications: Process pipelines for conveying corrosive media (such as acid, alkali, and salt solutions), linings for crude oil and refined oil conveying pipelines.
• Advantages: Excellent chemical stability, able to withstand various corrosive media; self-lubricating and non-scaling, ensuring the purity of conveyed media.
二、Emerging and High-Performance Fields
1. Sports and Athletics
• Applications: Side walls and panels of magic carpets (ski lifters) in ski resorts and dry ski fields; sliding surfaces in grass sliding fields and ice and snow parks.
• Advantages: Extremely strong surface self-lubrication with very low friction coefficient, providing a smooth motion experience; wear-resistant and impact-resistant, with a long service life, and causing minimal wear on sports equipment such as skis.
2. Material Conveying and Automation
• Applications: Pneumatic conveying pipelines for grains, feed, cereals, etc.; material conveying pipelines in food and pharmaceutical processing; guide rails and liners in automated production lines.
• Advantages: Smooth inner walls ensure good material flow, with little tendency to hang or clog; odorless and non-toxic, meeting food-grade requirements when using food-grade raw materials; good wear resistance, resulting in low maintenance costs.
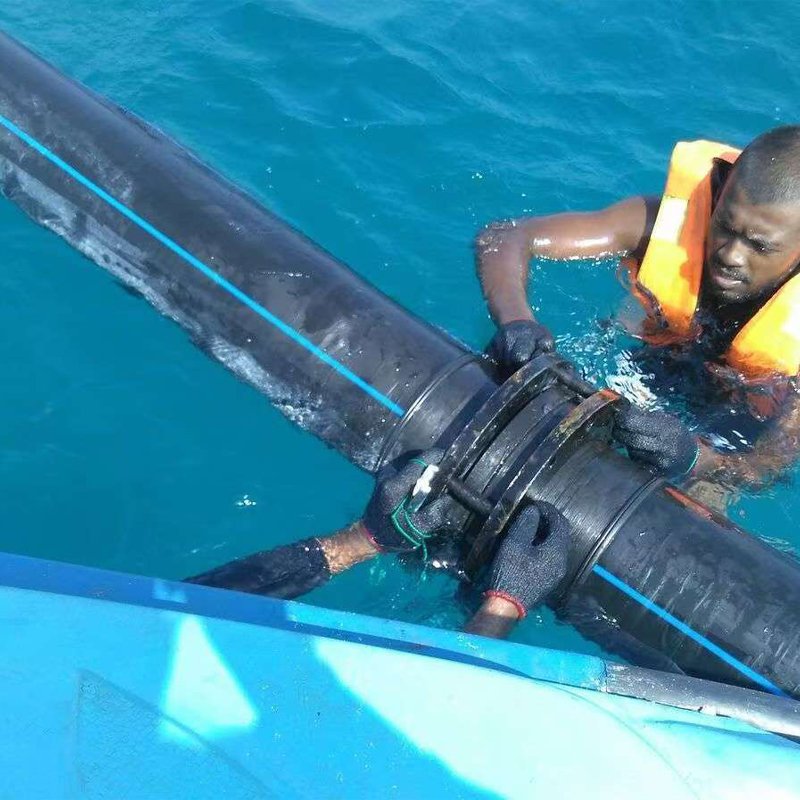
3. Ports and Marine Engineering
• Applications: Conveying linings of ship loading and unloading arms, port dredging pipelines, seawater desalination system pipelines.
• Advantages: Corrosion-resistant to seawater, with anti-ultraviolet properties achievable by adding modifiers; excellent wear resistance, extending equipment lifespan in harsh marine environments.
III. Unique Advantage Scenarios
1. The Ultimate Choice for Abrasion and Corrosion Resistance
In \”dual harsh\” environments where severe wear and chemical corrosion coexist, UHMW-PE pipes are a more reliable and economical solution compared to metals, ordinary plastics (such as PP, PVC), and ceramic materials.
2. Scenarios with High Product Protection Requirements
Thanks to its high lubricity and non-stick properties, when conveying easily damaged materials such as grains, plastic pellets, and high-end coatings, it can minimize material breakage and contamination to the greatest extent.
3. Scenarios Requiring Weight Reduction and Convenient Installation
Its density is only 1/8 that of steel, significantly reducing structural load and installation difficulty in mobile equipment such as dredgers and mining trucks, or in scenarios involving overhead pipeline installation.
IV. Limitations (To Be Considered When Selecting)
• Limited Temperature Resistance: Typically suitable for long-term use within a temperature range of -40°C to +80°C, not applicable for scenarios involving high-temperature steam or high-temperature medium transportation.
• Low Stiffness: Compared to metal materials, its modulus of elasticity is lower, making it unsuitable for load-bearing structural scenarios with extremely high rigidity requirements.
• Connection Technology Requirements: Requires specialized heat fusion butt welding or flange connection technologies, with specific requirements for construction processes.
• Higher Initial Cost: Raw material prices are higher than those of ordinary plastic pipes; however, considering its ultra-long service life and low maintenance cost, the total lifecycle cost is often lower.
In summary, ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMW-PE) pipes are not a universal material. However, in specific operating conditions characterized by \”high wear, high corrosion, and high requirements,\” they become a strategic engineering material that can significantly improve operational efficiency and reduce long-term operating costs due to their unique combination of properties. When selecting, the focus should be on evaluating whether their wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and self-lubrication characteristics are key to solving the core pain points of the current pipeline system.