Advantages and Disadvantages of Dredging Rubber Hoses
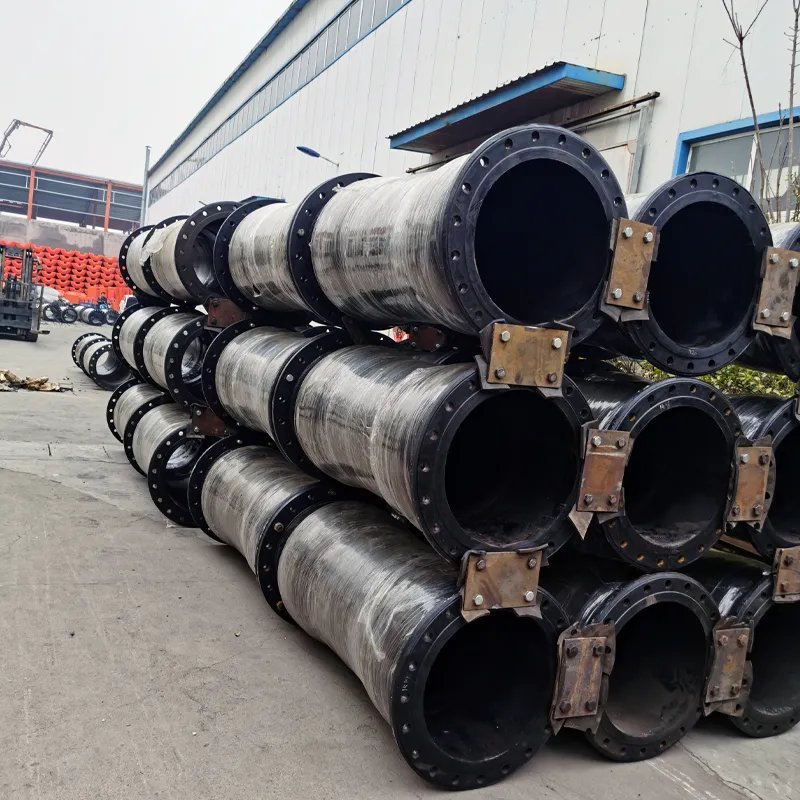

What is a rubber discharge pipe?
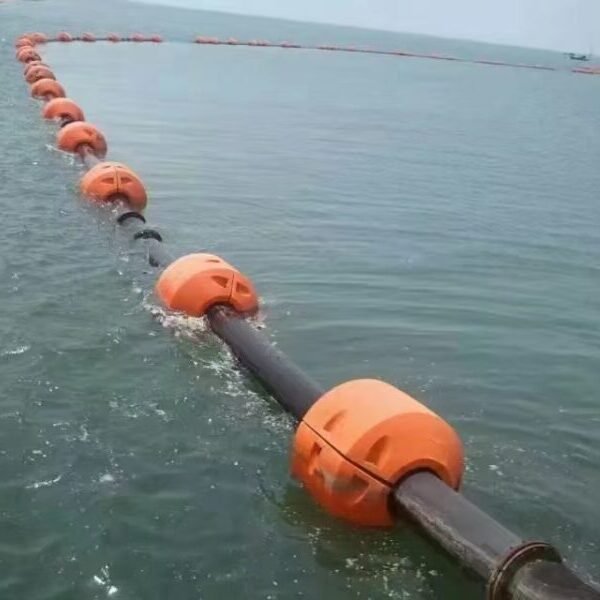
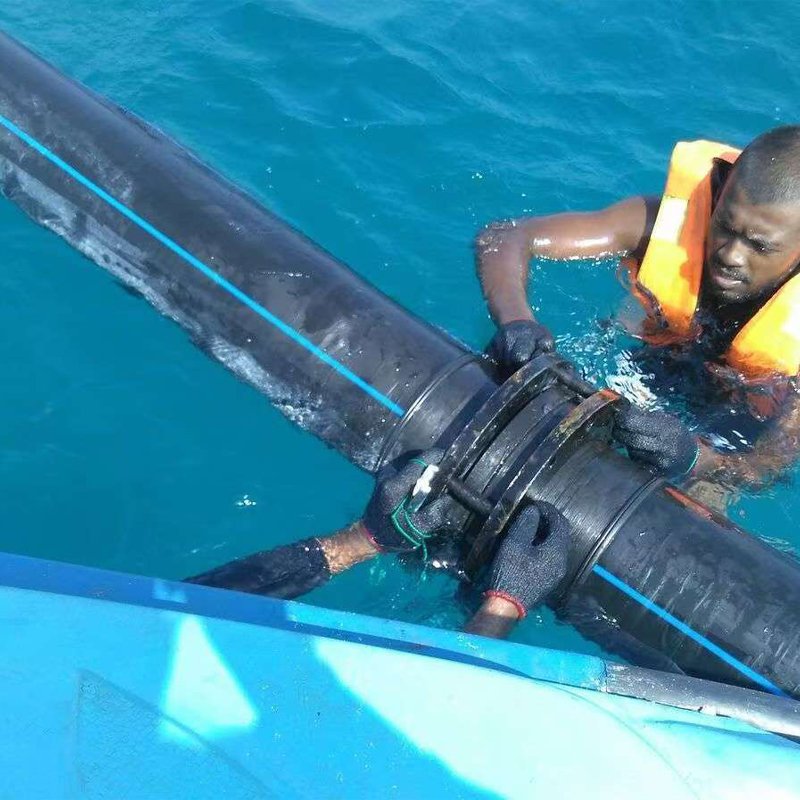
In dredging operations, a rubber discharge pipe is a pipeline connected to dredging equipment such as cutter suction dredgers and trailing suction hopper dredgers. It is used to transport a mixture of mud and sand (slurry). Typically functioning as a floating section, it floats on the water surface, conveying the slurry from the dredger to a designated reclamation area or discharge point.
Advantages of Rubber Hoses
1. Excellent Flexibility and Resistance to Bending
◦ This is its most core advantage. Rubber hoses can withstand frequent bending, twisting, and stretching, adapting well to the movement of ships, wave fluctuations, and water flow changes without permanent deformation or breakage. This is crucial for connecting continuously moving dredgers with relatively fixed shore pipes or underwater pipelines.
2. Superior Abrasion Resistance and Corrosion Resistance
◦ Abrasion Resistance: Slurry in dredging often contains a large amount of sand, gravel, and even small stones, which are highly abrasive. High-quality rubber hoses have wear-resistant materials (such as ceramics, high-wear-resistant rubber) embedded inside, resulting in a long service life.
◦ Corrosion Resistance: Rubber has natural resistance to seawater, freshwater, and most chemicals, making it less prone to rust or corrosion, with maintenance costs much lower than metal pipes.
3. Lightweight, Easy to Deploy and Recover
◦ Compared to steel pipes of the same specification, rubber hoses are much lighter. This makes them very convenient for水上 connection, disassembly, towing, and handling, significantly improving operational efficiency and reducing reliance on large lifting equipment.
4. High Buoyancy and Submersion Resistance
◦ Rubber hoses usually have a foamed buoyancy layer or hollow structure inside, giving them sufficient buoyancy to stably float on the water surface
Disadvantages of Rubber Hoses
1. Higher Initial Cost
◦ The single purchase cost of high-quality, large-diameter wear-resistant rubber hoses is usually higher than that of ordinary steel pipes. This can be a consideration for projects with limited budgets.
2. Relatively Weak Negative Pressure Resistance
◦ When pumping suddenly stops or pipeline layout is improper, negative pressure (vacuum) may occur inside the pipe. Rubber hose walls are prone to being sucked flat under negative pressure, leading to pipe blockage or even damage. Steel pipes do not have this problem. Therefore, special attention needs to be paid in system design to avoid negative pressure conditions.
3. Limited High-Temperature Performance
◦ Rubber ages acceleratedly when exposed to high temperatures for a long time, becoming hard, brittle, and losing elasticity and strength. If the medium being transported has excessively high temperature (e.g., certain industrial tailings), it will seriously affect its service life.
4. Poor Resistance to External Cutting and Tearing
◦ Although wear-resistant, rubber hose walls are relatively soft and are easily punctured, cut, or torn by sharp objects (such as shipwreck debris, sharp rocks, anchors, etc.). Such damage is usually more difficult to repair on-site compared to dents in steel pipes.
5. Long-Term Weather Resistance (Aging) Issues
◦ Long-term exposure to sunlight (ultraviolet rays), ozone, and extreme weather causes rubber to age, resulting in surface cracks, hardening, and a gradual decline in strength and elasticity. Regular inspections and replacement when necessary are required.
6. Limited Pressure-Bearing Capacity
◦ Although modern rubber hoses can withstand high pressures, their maximum working pressure is generally still lower than that of thick-walled steel pipes of the same specifications. For long-distance transportation projects requiring ultra-high pumping pressure, steel pipes or composite pipes may need to be used.