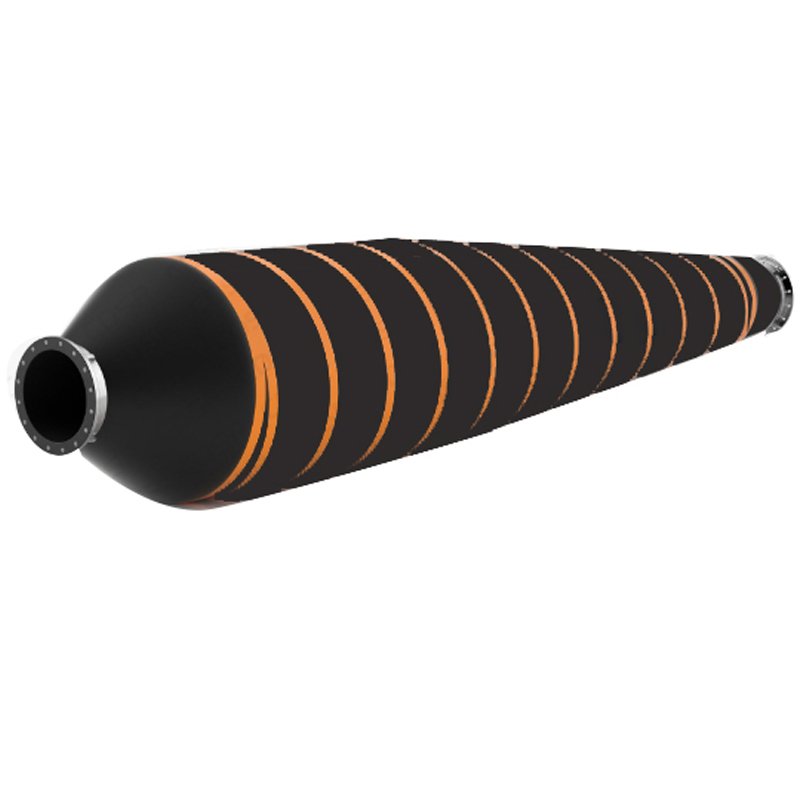
How to choose the right armoured dredging discharge hose

Choosing the right armoured dredging discharge hose involves considering several factors such as working environment, medium characteristics, pressure requirements, abrasion resistance, and connection methods. Here is a detailed selection guide:
1. Determine the application scenario:
– Dredging type: riverbed cleaning, underwater excavation, port construction, mine tailings transportation, etc.
– Medium characteristics:
– Material being transported: mud, gravel, sludge, slurry, etc.
– Particle size and hardness (such as sharp stones or highly abrasive substances).
– Medium temperature (ambient or high temperature).
– Chemical properties (corrosive nature, such as seawater or acid-base environments).
2. Key performance parameters:
(1) Pressure rating:
– Working pressure: Select the hose’s pressure tolerance based on the maximum pump system pressure (e.g., 10 bar, 15 bar, 25 bar).
– Burst pressure: The hose’s maximum pressure capacity, typically 2 to 4 times the working pressure.
(2) Abrasion resistance:
– Liner material: High-abrasion-resistant rubber (such as natural rubber NR, styrene-butadiene rubber SBR, or polyurethane PU) is commonly used.
– Armoring layer: Reinforced with steel wire or spiral steel bands to protect the hose from tearing or flattening.
– Thickness of the abrasion-resistant layer: The thicker the lining, the stronger the resistance to abrasion (e.g., over 10mm for highly abrasive media).
(3) Bend radius and flexibility:
– Must accommodate site bending needs to avoid damage from excessive bending.
– Armoring layer design must balance flexibility and pressure resistance.
(4) Size and length:
– Inner diameter (ID): Common specifications range from 100mm to 1200mm, depending on flow requirements.
– Length: Standard lengths usually range from 10m to 20m, but custom lengths are also available.
3. Structural design:
– Inner layer (liner): Abrasion-resistant rubber, corrosion-resistant.
– Reinforcement layer:
– Multiple layers of high-strength fibers (such as polyester or aramid) or steel wire braiding/wrapping.
– Armoring layer: Spiral steel wire or steel band (for negative pressure resistance and external impact).
– Outer layer (cover): UV-resistant, weather-resistant rubber or synthetic materials (such as NBR, EPDM).
4. Environmental adaptability:
– Weather resistance: Outdoor use requires UV and ozone resistance.
– Buoyancy requirement: Whether floating hose or submerged hose is needed.
– Temperature range: Special materials required for extreme high or low temperatures.
5. Connection method:
– Flange connections: Standard flanges (such as DIN, ANSI), quick couplings (camlock).
– Custom ends: Designed according to equipment interface requirements.
6. Certification and standards:
– Compliance with industry standards: Such as ISO 4649 (abrasion testing), EN ISO 10823 (dynamic pressure testing).
– Marine engineering requires salt spray resistance and seawater corrosion resistance.
7. Brand and supplier:
– Renowned brands: Such as Goodyear, Continental, Trelleborg, Kuri Tec, Weifang Flex, etc.
– Supplier should provide:
– Technical data sheet (including pressure, bend radius, abrasion data).
– Case references (similar project experience).
– After-sales support (such as replacement, maintenance services).
8. Cost and lifespan trade-off:
– High-abrasion, high-pressure hoses have higher initial costs but reduce replacement frequency over time.
– Avoid choosing hoses that do not meet the working conditions to save costs, which may lead to frequent damage.
Recommended steps:
1. Clarify requirements: medium, pressure, flow rate, environmental conditions.
2. Consult suppliers: provide details of the operating conditions to obtain customized solutions.
3. Sample testing: field trials to verify abrasion resistance and pressure resistance.
4. Compare and choose: make decisions based on overall performance, price, and service.